ELK SOC Lab Setup and Configuration – 01/10/2024
In this lab, I set up an ELK stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) SOC on Vultr to simulate the implementation and configuration of a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system within a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). The project included configuring various systems, simulating a brute force attack using Mythic C2, and creating custom dashboards for alerting and monitoring security events. Below is a detailed step-by-step breakdown of the lab configuration.
This is the Lab logical diagram:
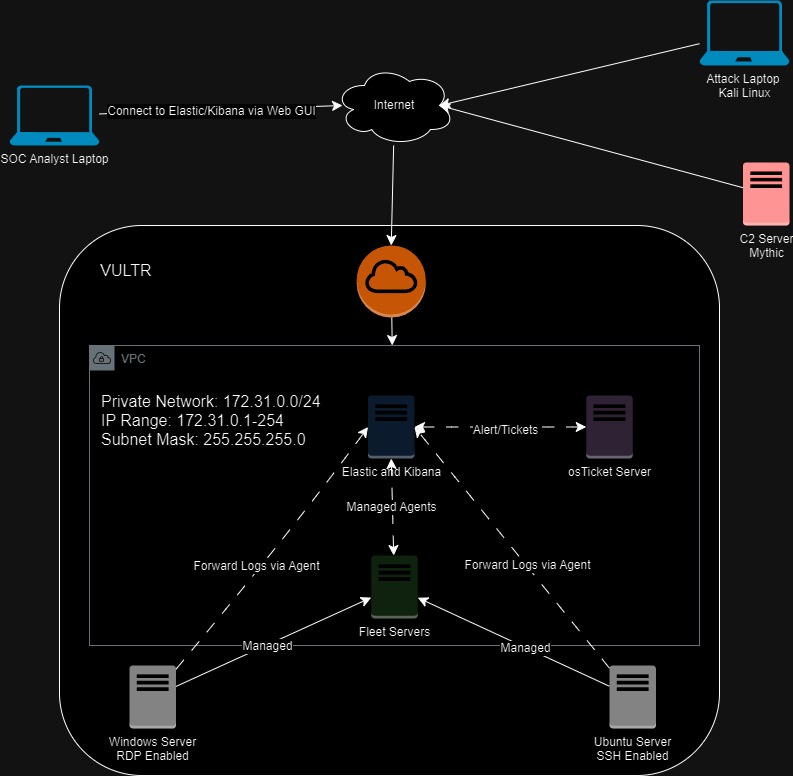
1. VPC and Elasticsearch Server Configuration:
VPC Setup:
- Created a VPC 2.0 network on Vultr in the Sydney region with the network address
172.31.0.0/24.
Elasticsearch Installation:
- Deployed an Ubuntu 22.04 LTS VM named
ELK-SOCLabwith 80GB storage. - Downloaded the Elasticsearch DEB package using
wgetand installed it on the VM. - Modified the Elasticsearch configuration (
/etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml) to change thelocalhostto the public IP address of the VM and enabled the HTTP port. - Configured firewall rules in Vultr to only allow access from my IP address.
Kibana Installation:
- Installed Kibana and configured it by editing
/etc/kibana/kibana.yml, setting the server port and binding it to the public IP address of the VM. - Allowed Kibana traffic on port 5601 using
ufwand set up firewall rules in Vultr to limit access to my IP. - Connected to Kibana via the public IP (
http://[VM public IP]:5601), used the Elasticsearch enrollment token, and set up encryption keys for Kibana security.
2. Windows Client Configuration:
- Deployed a Windows Server VM on Vultr in the Sydney region, choosing the shared CPU option and the Windows Standard Image.
- Disabled auto-backups and IPv6.
- Accessed the Windows Server using the Vultr console and installed Sysmon (System Monitor) to enhance logging capabilities.
- Integrated the Windows Server with the ELK stack by adding Sysmon logs through the Elastic Agent, using the Windows Event Logs integration for deeper visibility into Windows events.
3. Fleet Server Configuration:
Fleet Server Setup:
- Deployed another Ubuntu 22.04 VM named
ELKSOCLab-FleetServerand installed the Elastic Agent on it, designating it as a Fleet Server. - Created a Fleet Server Policy within Elastic and attached the server to this policy.
Agent Deployment:
- Created a new Fleet Windows Policy (
ELK-SOCLAB-omar) for Windows log collection and deployed the Elastic Agent on the Windows Server, allowing for real-time log ingestion.
4. Data Ingestion and Custom Integrations:
Windows Data Ingestion:
- Added custom Windows Event Logs in Elasticsearch, including Sysmon and Microsoft Defender logs, to provide more visibility into system activities and security events.
- Created two integration policies:
SOCLAB-WIN-Defenderfor Microsoft Defender logs andSOCLAB-WIN-SYSMONfor Sysmon logs.
Ubuntu Server Configuration:
- Deployed an additional Ubuntu VM named
ELKSOCLAB-Linux-Omar, installed the Elastic Agent, and added it to the Fleet Server to ingest Linux logs into Elasticsearch for further analysis.
5. Custom Dashboards:
Dashboard 1:
- Monitored failed and successful authentication attempts for SSH and RDP with the following visualizations:
- SSH Failed/Successful Authentication Maps
- SSH Failed/Successful Activity Tables
- RDP Failed/Successful Authentication Maps
- RDP Failed/Successful Activity Tables
Dashboard 2:
- Focused on process and network activity, including:
- Process Created Table (to track newly created processes)
- Process Initiated Network Table (to monitor network connections made by processes)
- Microsoft Defender Disabled Table (to detect if Windows Defender was disabled)
6. Mythic C2 Server and Agent Setup:
Mythic Server Deployment:
- Deployed a new Ubuntu VM on Vultr named
ELKSOCLab-Mythicand installed Mythic C2 using Docker.
This is the Attack diagram:
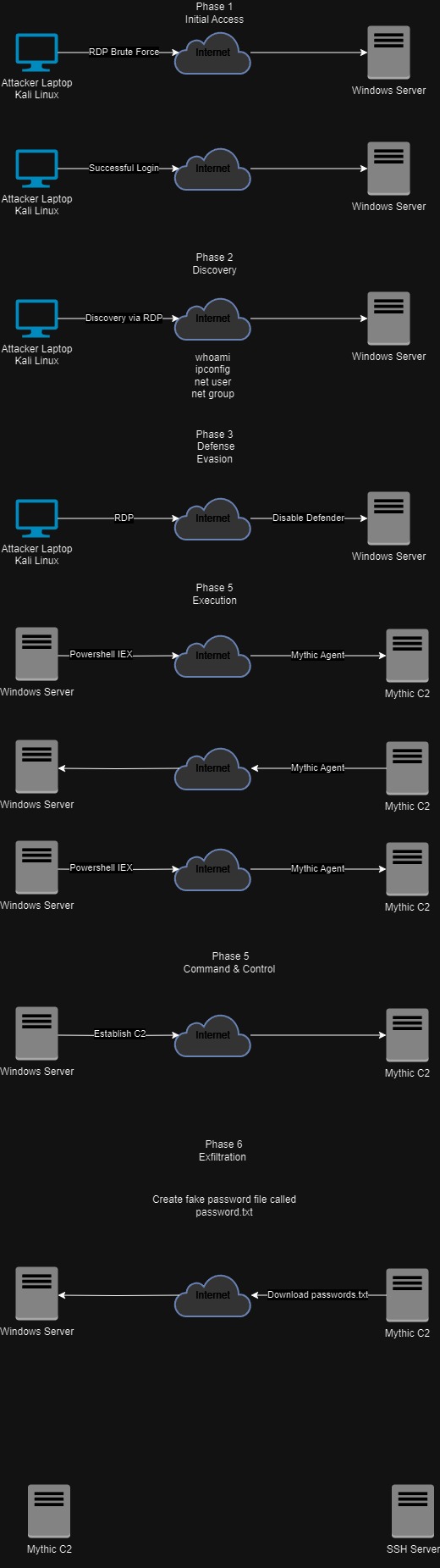
Mythic Agent Configuration:
- Created an Apollo Mythic agent with an HTTP profile, enabling all commands. The agent was configured to call back to the Mythic Server, simulating a compromised Windows system.
- Named the agent
svchost.exeto blend in with legitimate processes on the target system.
7. Brute Force Attack Simulation:
Kali Linux Setup:
- Installed Kali Linux on VirtualBox, updated the repositories, and prepared it for the attack.
- Used Crowbar to perform a brute force attack on the Windows Server by leveraging weak passwords.
- After gaining access, disabled Windows Defender and executed a Python HTTP server to deliver the C2 Mythic agent to the compromised Windows system.
- Successfully established a connection between the Mythic agent and the Mythic Server, simulating command and control operations.
8. osTicket Setup and Integration:
osTicket Installation:
- Deployed a new Windows Server on Vultr (IP:
172.31.0.5) for osTicket. - Installed XAMPP with PHP 8.2.12 and configured it to work with osTicket.
- Set up the osTicket web interface, creating a database for ticket management.
- Configured the necessary firewall rules in Windows Defender to allow incoming traffic on ports 80 and 443.
osTicket and ELK Integration:
- Created an API key on the osTicket server and integrated it with ELK using a webhook for secure communication.
- Used this setup to automatically generate tickets in osTicket based on security alerts triggered in the ELK stack.